Welcome to the Guam Radiology Consultants Women’s Imaging Center
 At the GRC Women’s Imaging Center, we understand that women have unique healthcare concerns. We believe women deserve access to the specialized diagnostic services they need to prevent, detect and treat those ailments most common to them.
At the GRC Women’s Imaging Center, we understand that women have unique healthcare concerns. We believe women deserve access to the specialized diagnostic services they need to prevent, detect and treat those ailments most common to them.
GRC’s Women’s Imaging Center is designed to ensure that your specific health needs are addressed in a comprehensive and compassionate way. We have Guam’s most experienced women’s imaging team with Radiologists who have specialized in mammography as well as certified mammography, ultrasound and MRI technologists to ensure that your testing is accurate, comfortable and timely.
We are committed to meeting the diagnostic needs of women, including screening and diagnostic mammography, pelvic and breast ultrasound, breast MRI and bone density screening. We also offer advanced techniques: ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration and ultrasound-guided core biopsy.
Why GRC Women’s Imaging Center…
The Guam Radiology Consultants Women’s Imaging Center is committed to providing individualized, innovative, state-of-the-art health care to women. Our center offers treatment of the whole woman, including breast and other female imaging services. The Radiologists, Technologists, and Medical Assistants, are closely involved in the diagnostic exam of each patient.
We recognize and respond with respect and dignity to individual medical, physical, and emotional needs. We value the uniqueness of each patient. We will communicate openly and honestly, and practice ethically in all relationships with those we serve. We realize that our work makes a difference in our patient’s lives and in our community. We exist to provide care to all those who come to us. It is a privilege for us to participate in the care of all our patients.
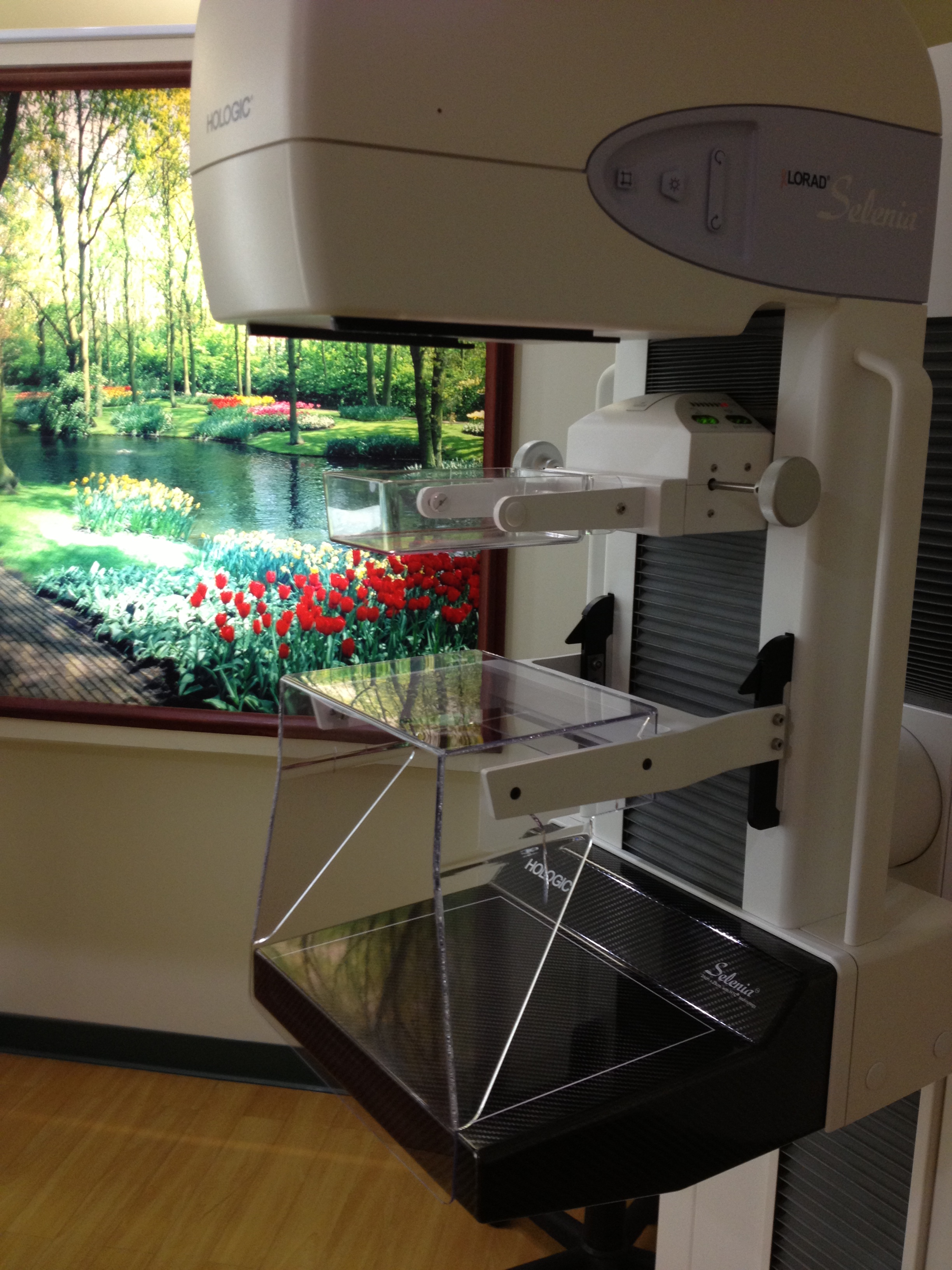
What is Mammogram?
A mammogram is an x-ray examination of the breast, used to detect and diagnose breast diseases.
A screening mammogram usually involves two views of each breast. Diagnostic mammography involves additional views of the breast, and is used when an abnormality is found during screening, or in women who have breast complaint, such as a breast mass, nipple discharge, breast pain, or skin irritation.
Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool
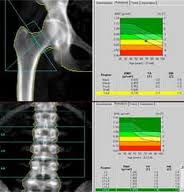
What is Bone Densitometry?
A bone densitometry scan is a special type of X-ray test used to measure the calcium content of the bone.
The examination is also called a dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scan or QDR scan. The DEXA scan is the established standard for measuring bone mineral density (BMD).
This is a simple, quick and non-invasive medical test, which involves exposing particular parts of the body to very small amounts of ionisation radiation.
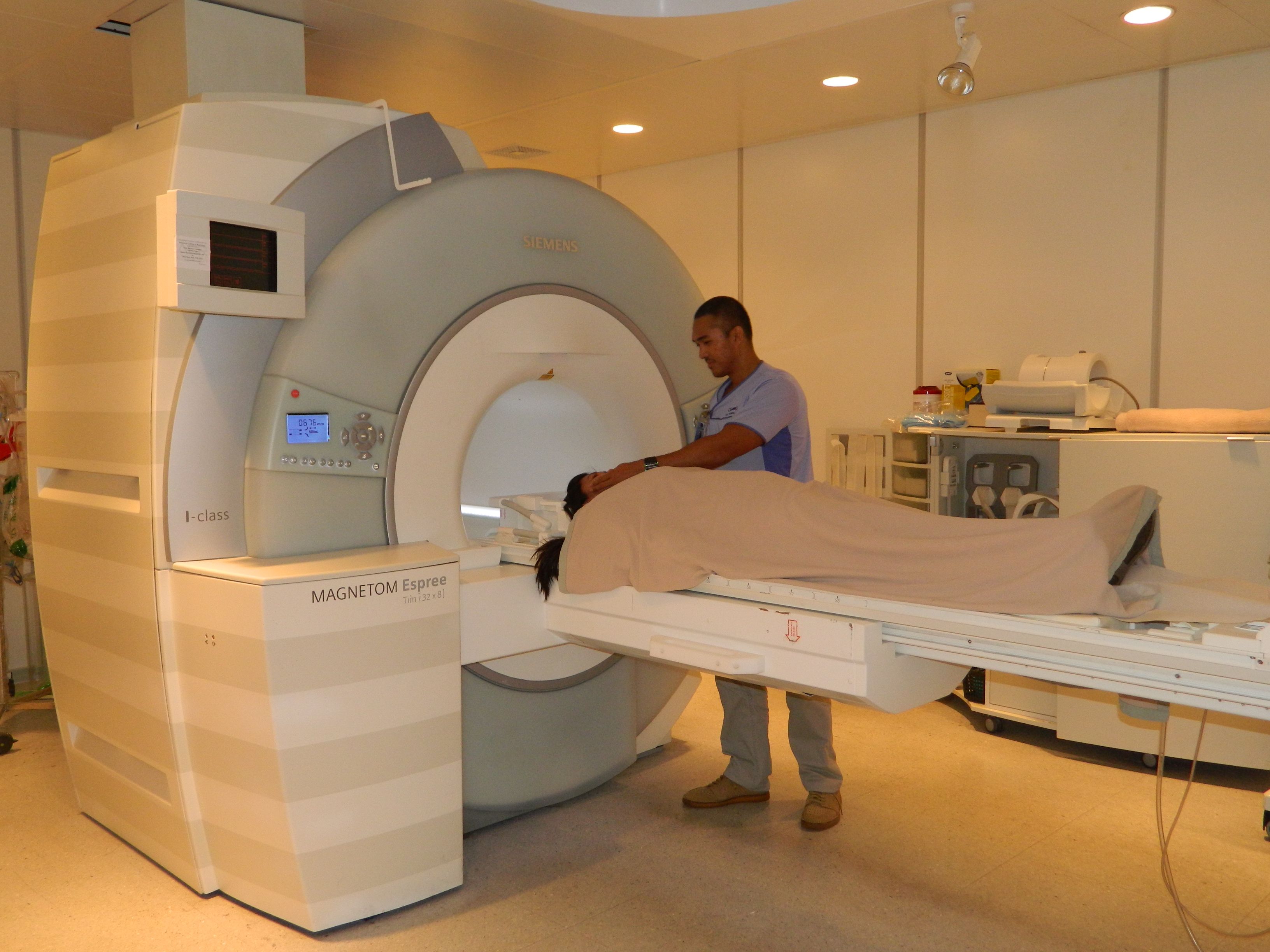
Mammogram or Breast MRI
- Breast MRI and mammogram are both noninvasive diagnostic screening tests used for early detection
- Mammograms are less expensive, faster and effective for the detection of abnormalities in the breast that are not yet specifically identified
- MRIs are more sensitive for the detection of invasive cancers
- Breast MRI should be considered for women with personal history or family history of breast cancer
- In many cases, breast MRIs are used to evaluate abnormalities detected on Mammogram and ultrasound
- MRI’s can be used to examine the integrity of the breast implant
Understanding breast biopsy
You do a breast self-exam every month and have a mammogram every year. Everything has always been fine, but then your doctor calls to say the results of your last mammogram were not normal and you need to have a breast biopsy. Your first thought is - “Why? Do I have breast cancer?”
A biopsy can be used to diagnose breast cancer, but most lumps are not cancer. In fact, results for four out of five biopsies are non-malignant. So if you do not have cancer, what do you have?
Benign or non-cancerous breast conditions fall into two main categories, neither of which is life-threatening. Fibrocystic changes in the breast often occur before a period, causing cysts and areas of lumps, tenderness or nipple discharge. Benign breast tumors are areas of breast cells that have grown abnormally and rapidly to form lumps that may be uncomfortable, but they do not spread outside the breast to other organs.
A breast biopsy involves taking a sample of connective tissue, fat lobules or milk ducts to check for cancer or other breast conditions. There are several ways to perform a biopsy. Your doctor will recommend the procedure that is right for you.
During a fine-needle aspiration biopsy, a thin needle is passed through the skin to the lump and cells are removed for examination. A needle biopsy can be done to see if the lump is solid or a fluid-filled cyst. If there is no fluid, another type of biopsy is done; if it is a cyst, it should go away after the fluid is removed.
A slightly larger, hollow needle with a special tip is used during a core needle biopsy. During this procedure, three to six tissue samples are removed, sometimes using vacuum suction. A core needle biopsy is more likely to provide definite results because more tissue is removed for study. During a fine-needle or core needle biopsy, the doctor usually guides the needle to the abnormal area by palpating (feeling) the lump.
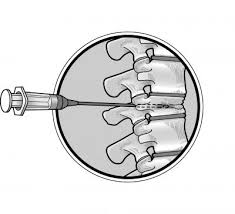
If the area being studied is too small to be felt, the doctor may perform a stereotactic needle biopsy using X-ray images to locate where the sample will be taken. Ultrasound also may be used to guide the needle into very small tumors or cysts.
A surgical biopsy involves making an incision to remove part of the lump (incisional biopsy), or the entire lump and some surrounding tissue (excisional biopsy or lumpectomy). If the lump is too small to be located easily, a flexible wire may be inserted into the suspicious area using X-rays to help guide the surgeon to the lesion. This is called wire localization.
If your doctor recommends that you have a biopsy, do not assume the worst. Approximately one million American women are diagnosed with benign breast disease each year. Breast biopsy is generally considered to be a safe, outpatient procedure. If you have any questions about your biopsy, talk with your doctor or get a second pathology review of your results. Even if you do not have cancer, it is important to have regular mammograms, watch for any changes in your breasts, and see your doctor for routine breast exams.
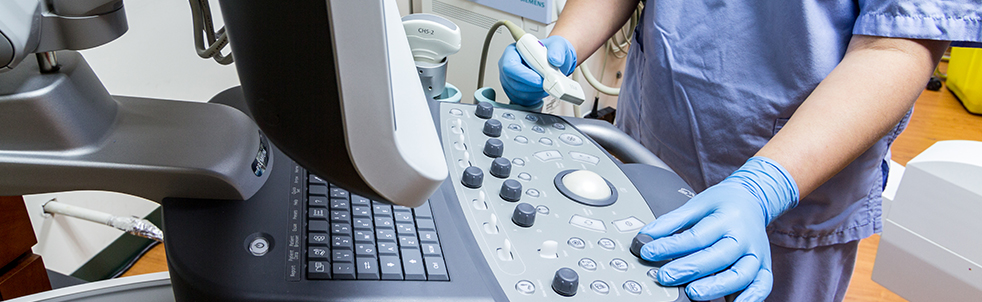
What is breast Ultrasound?
Ultrasound imaging, also called ultrasound scanning or sonography, is a method of obtaining images from inside the human body through the use of high-frequency sound waves. The reflected sound wave echoes are recorded and displayed as a real-time visual image. No ionizing radiation (x-ray) is involved in ultrasound imaging. Ultrasound is a useful way of examining many of the body’s internal organs, including but not limited to the heart, liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, kidneys and bladder. At the Women’s Imaging Center we offer breast ultrasound. Breast ultrasounds are usually performed in conjunction with a diagnostic mammogram or separately. In some cases it is not possible to tell from the imaging studies alone whether a growth is benign or cancerous.
| Teleradiology | Women's Imaging Center |
|---|---|
|
At the GRC Women’s Imaging Center, we understand that women have unique healthcare concerns. We believe women deserve access to the specialized diagnostic services they need to prevent, detect and treat those ailments most common to them. GRC’s Women’s Imaging Center is designed to ensure that your specific health needs are addressed in a comprehensive and compassionate way. We have Guam’s most experienced women’s imaging team with Radiologists who have specialized in mammography as well as certified mammography, ultrasound and MRI technologists to ensure that your testing is accurate, comfortable and timely Read more... |
Contact Us
|
Guam Radiology Consultants |
Office Hours: Mon – Fri: 8AM – 6PM Sat: 8AM – 1PM |